In high-voltage electrical equipment, there are a large number of oil-filled equipment (such as transformers, transformers, oil circuit breakers). The main role of the insulating oil in these devices is as follows.
(1) so that the oil-filled equipment has a good thermal cycle circuit, in order to achieve the purpose of cooling exothermic. In the oil-immersed transformer, it is through the oil to the transformer heat transfer to the oil tank and cooling device, and then by the surrounding air or cooling water for cooling.
(2) Increase phase to phase, layer to layer, as well as the main insulation capacity of the equipment, improve the insulation strength of the equipment. For example, oil circuit breaker insulation between the same conductive circuit breakers.
(3) Insulate the equipment insulation from contact with the air to prevent the occurrence of oxidation and moisture immersion, to ensure that the insulation is not reduced. In particular, transformers, capacitors in the insulating oil to prevent moisture intrusion, but also fill the voids in the solid insulating material, so that the insulation of the equipment is strengthened.
(4) in the oil circuit device, in addition to insulating oil as an insulating medium, but also as an arc extinguishing medium to prevent the expansion of the arc, and prompt the arc to extinguish quickly.

Electrical insulating oil
(1) classification. Electrical insulating oil, also known as electrical oil, including transformer oil, oil circuit breaker oil, capacitor oil and cable oil and other 4 types of oil.
(1) transformer oil is a low viscosity oil, used in transformers and other equipment for cooling and insulation.
(2) oil circuit breaker oil is used for oil-immersed circuit breakers a kind of insulating oil, in addition to insulation and cooling effect, but also can play a role in eliminating the circuit cut off generated by the arc (sparks).
(3) capacitor oil is used for capacitors (mainly power capacitors or electrostatic capacitors), the role of insulation impregnation or moisture barrier oil.
(4) cable oil is used for cable insulation, impregnation and cooling effect of refined lubricating oil, or lubricating oil and other thickening agents (such as soft wax, resin, polymer or asphalt, etc.) of the mixture. Among them, transformer oil and oil circuit breaker oil accounted for about 80% of the whole electrical appliances oil
Insulation Oil Breakdown Testing ( BDV Testing )
Why conduct the transformer oil breakdown testing ?
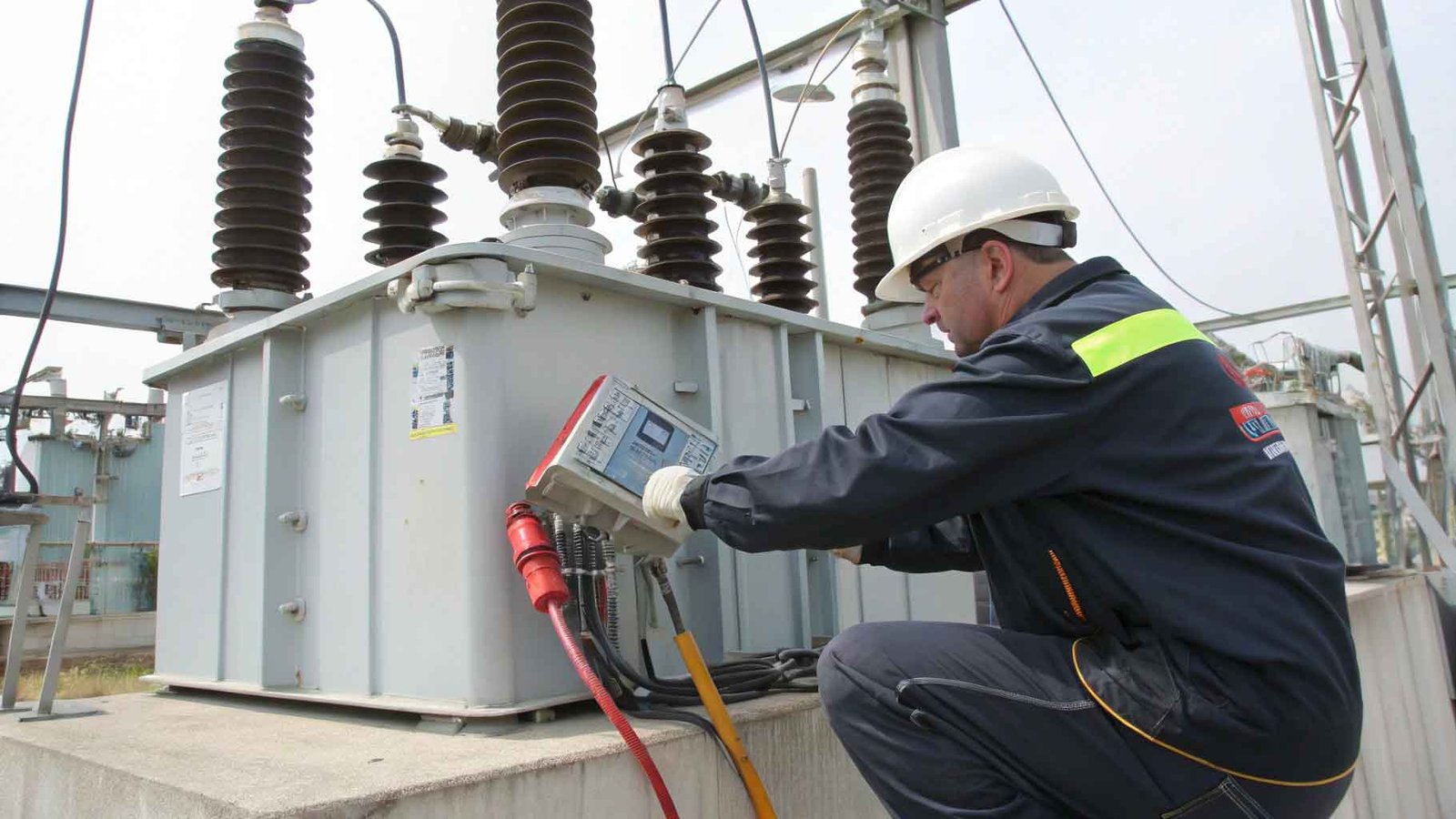
It is very important to conduct an insulating oil withstand pressure test on transformer oil, this is because transformer oil as a key insulating medium in the power system, its performance directly affects the safe operation and service life of the transformer. Below are a few of the main reasons for conducting an insulating oil withstand pressure test:
- Evaluating insulating properties: The withstand voltage test evaluates whether the insulating properties of the transformer oil meet the requirements. If the insulating properties of the oil deteriorate, this may lead to an electrical breakdown and equipment failure.
- Preventing malfunctions: Through regular testing, potential problems in the oil, such as moisture, impurities or aging products, can be detected in time, thus preventing possible malfunctions and accidents.
- Extension of equipment life: Good insulation reduces arcing and partial discharges within the equipment, thus extending the service life of the transformer.
- Monitoring the aging process: transformer oil ages during operation, and voltage testing helps to monitor this process to ensure that the aging of the oil does not affect its insulating properties.
- Compliance with safety standards: Safety standards in the power industry require that transformer oils be tested regularly for voltage withstand to ensure the safety of equipment operation.
- Maintaining power system stability: The insulating properties of transformer oil are critical to the stability of power systems. Pressure withstand testing helps to maintain the stability of the power system.
- Influence of environmental factors: As you mentioned, transformer oils are affected by oxygen, humidity, high temperature, sunlight, strong electric fields and impurities during operation, all of which may cause oil performance to deteriorate. Pressure withstand tests can assess the effect of these factors on oil performance.
- Economy: Through regular testing and maintenance, repair costs and power outage losses due to equipment failure can be reduced, which is very economical
The definition of Insulation Oil Breakdown Testing ( BDV Testing )
The dielectric strength test for transformer insulating oil is an electrical performance evaluation defined as the measurement of the maximum voltage that the oil can withstand between two electrodes under specified test conditions before electrical breakdown occurs. The results of this test are expressed in kilovolts per millimeter (kV/mm) and are referred to as dielectric strength or insulation strength. This measurement is a key indicator for assessing the quality of the insulating oil, its level of contamination, and its aging status. It is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of power transformers and preventing electrical failures.
The principle of BDV Testing
Some initial free electrons are naturally present in pure transformer oil. These free electrons serve as the starting point for initiating the breakdown process when an electric field is applied. In the presence of this electric field, the free electrons begin to move. The acceleration of these electrons allows them to gain sufficient energy to collide with other molecules or atoms, generating more free electrons in a process known as impact ionization.
As the strength of the electric field increases, more electrons are accelerated and contribute to impact ionization, leading to a rapid increase in the number of free electrons. When the electric field strength reaches a critical level, the quantity of free electrons in the oil becomes sufficient to form a conductive channel, resulting in a loss of the oil’s insulating properties and ultimately causing breakdown.
During the breakdown voltage (BDV) test, the voltage applied to the oil sample is gradually increased until breakdown occurs, and the voltage value at this point is recorded as the oil breakdown voltage.
Insulation Oil Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is a measure of the insulating oil in the electrical equipment to withstand the voltage and not be destroyed, but also to assess the performance of the insulating oil is a key indicator of good or bad, can reflect the oil is dirty, moisture and aging and other leading to a decline in the insulating properties of the situation
Oil Breakdown Voltage
Definition: Breakdown voltage is the voltage level at which electrical breakdown occurs between two electrodes under specified test conditions. Electrical breakdown happens when the electric field strength exceeds the insulating strength of the material, leading to a loss of insulating properties and a sudden increase in current.
Influencing Factors:
- Electric Field Strength: Higher electric field strengths result in higher breakdown voltages.
- Material Properties: Different insulating materials exhibit varying breakdown voltages.
- Temperature: Increasing temperature may decrease the breakdown voltage of the insulating material.
- Humidity: Elevated humidity levels can reduce the breakdown voltage of certain insulating materials.
- Electrode Shape and Distance: The geometry of the electrodes and the distance between them also influence the breakdown voltage.
- Dielectric Strength
- Definition: Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field strength that a material can withstand per unit thickness (or distance) without undergoing breakdown. It is typically expressed in kilovolts per millimeter (kV/mm) and serves as a crucial metric for assessing the insulation properties of materials.
Calculation Formula:
Dielectric Strength=Breakdown Voltage/ Distance Between Electrodes
Influencing Factors:
- Material Type: Different insulating materials possess distinct dielectric strengths.
- Temperature: Dielectric strength generally decreases as temperature increases.
- Humidity: Higher humidity can diminish the dielectric strength of some materials.
- Electrode Material and Shape: The material and design of the electrodes can also affect dielectric strength measurements.
- Dielectric strength is a critical parameter in the design and selection of insulation materials, particularly in high-voltage power equipment such as transformers, cables, and capacitors. Materials with high dielectric strength offer superior insulation protection, reducing the risk of electrical breakdown and enhancing the reliability and safety of the equipment.
How do you test the breakdown voltage of oil ?
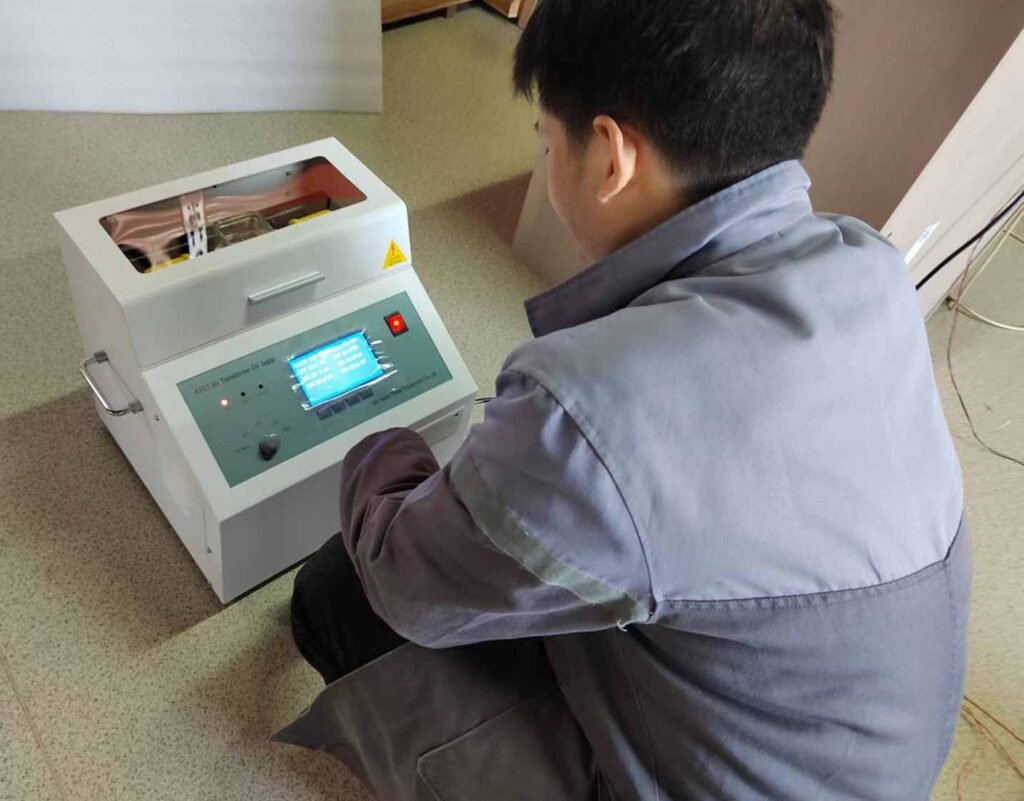
Transformer oil breakdown tester step
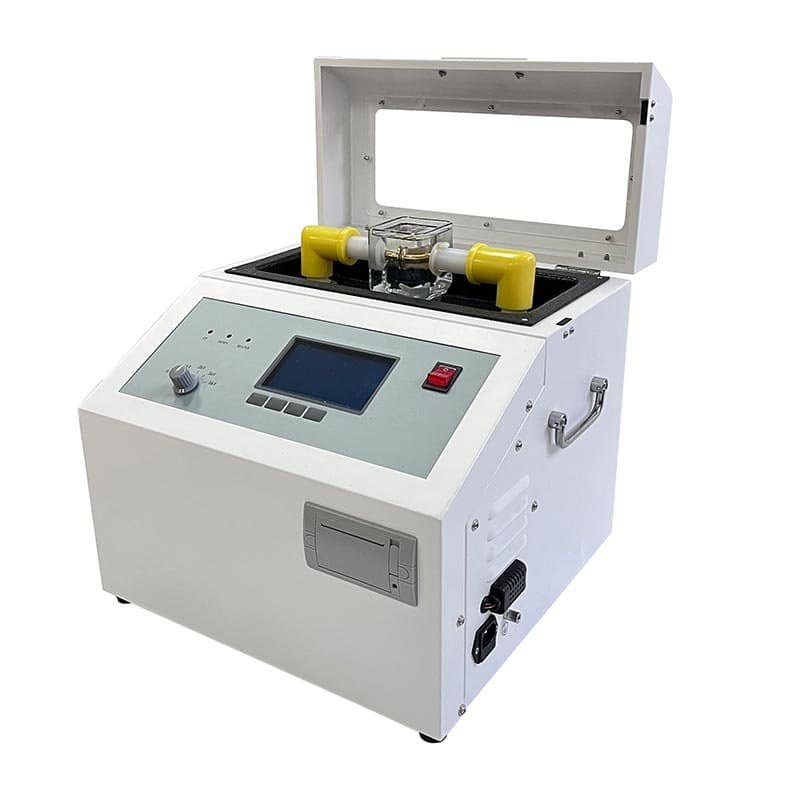

Dielectric strength testing of transformer oil is a standardized experimental procedure used to evaluate the insulating properties of oil. The following are the specific steps for the pressurization test:
1. Preparation:
- Ensure that the test environment meets the requirements, such as temperature and humidity control in the appropriate range.
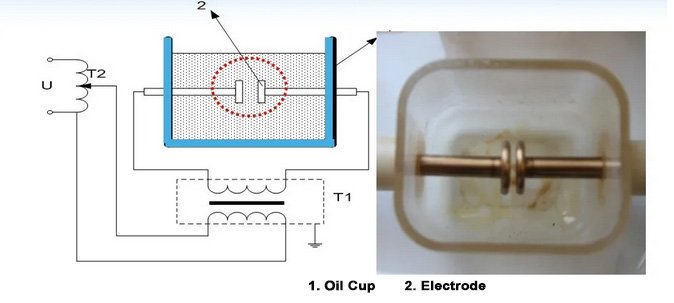
- Prepare clean specimen cups and electrodes, make sure that they are free from contamination and that the inside of the specimen cups and the electrode surfaces are dry.
- Take appropriate amount of oil sample and pour it into the sample cup, the amount of oil sample should be able to cover the electrode completely.
2. Set the test parameters:
- Place the sample cup on the test apparatus, make sure that the electrodes are correctly installed and that the distance between the electrodes meets the standard requirements.
- Set up the test apparatus to ensure that an AC voltage of 50 Hz is applied.
- Adjust the ramp-up rate so that it is controlled at (2 ± 0.2) kV/s.
3. Start the test:
- Start the test apparatus and begin to gradually increase the voltage.
- Observe the voltmeter and ammeter, and record the voltage value when the voltage rises to the point where breakdown occurs in the oil gap.
4. Record the breakdown voltage:
- When the oil gap breaks down, the test instrument will record the voltage value at this time.
- Breakdown refers to the phenomenon that the oil sample loses its insulating property under the action of electric field and the current increases sharply.
5. Repeat the test:
Repeat the above steps for 6 separate tests, refilling the oil sample is required after each test and ensuring that the electrodes and specimen cups are clean.
6. Calculate the average value:
Add the breakdown voltage values obtained from the 6 tests and divide by 6 to obtain the average value.
This average value is the dielectric strength of the oil sample.
7.Analysis of results:
The average value of the dielectric strength is analyzed and compared with standard or historical data to assess whether the insulation properties of the oil sample have deteriorated.
If the dielectric strength is below the standard value, it may indicate that the oil sample is dirty, damp or aged.
8.Test Report:
Prepare a test report that includes test conditions, breakdown voltage values for each test, calculated average values, and any observed anomalies.






